Mitochondria-associated AMPK (mitoAMPK)
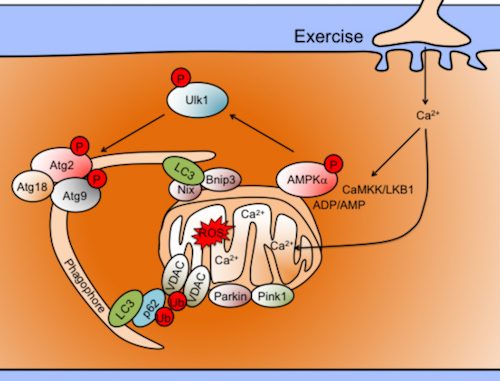
5' AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) is a key sensor for maintaining metabolic homoeostasis, linking energetic stress to mitochondrial remodeling and functional adaptations under various conditions. It has been known for years that the α2β2γ3 trimeric holoenzyme is the main AMPK form expressed in skeletal muscle and is activated by endurance exercise for adaptations. However, it is still not clear how AMPK activation instructs with aforementioned specificity for mitochondrial remodeling. The Yan Lab has used bioinformatics and obtained clues that a different form of AMPK might be localized at mitochondria (referred as mitoAMPK). By biochemical purification, the lab has obtained direct evidence that a unique combination of AMPK subunits are physically associated with mitochondria in various mouse tissues/organs and in human skeletal muscle. The team employs CRISPR/Cas9-mediated gene editing as well as molecular imaging to investigate the mechanisms that control the activation of mitoAMPK as well as its functional role in mitochondrial remodeling and contractile and metabolic adaptations. The lab's research has obtained the first direct evidence of the importance of Atg2-Atg18/Atg9 autophagy complex in the maintenance of mitochondrial integrity and, regulation of heart and muscle functions in Drosophila, raising the possibility of augmenting Atg2-Atg18/Atg9 activity in promoting mitochondrial health and, muscle and heart function. The Yan Lab's data in mouse skeletal muscle indicate that exerciseinduced mitophagy occurs in the absence of stabilization of Pink1 on mitochondria, pointing to a different control mechanism for exercise-induced mitophagy.
Publications
Drake JC, Yan Z. Mitophagy in maintaining skeletal muscle mitochondrial proteostasis and metabolic health with ageing. J Physiol. 2017 Oct 15;595(20):6391-6399. doi: 10.1113/JP274337. Epub 2017 Sep 24. Review. PubMed PMID: 28795394; PubMed Central PMCID: PMC5638883.
Drake JC, Laker RC, Wilson RJ, Zhang M, Yan Z. Exercise-induced mitophagy in skeletal muscle occurs in the absence of stabilization of Pink1 on mitochondria. Cell Cycle. 2018 Dec 17. doi: 10.1080/15384101.2018.1559556. [Epub ahead of print] PubMed PMID: 30558471.
Xu P, Damschroder D, Zhang M, Ryall KA, Adler PN, Saucerman JJ, Wessells RJ, Yan Z. Atg2, Atg9 and Atg18 in mitochondrial integrity, cardiac function and healthspan in Drosophila. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2018 Dec 17;127:116-124. doi: 10.1016/j.yjmcc.2018.12.006. [Epub ahead of print] PubMed PMID: 30571977.